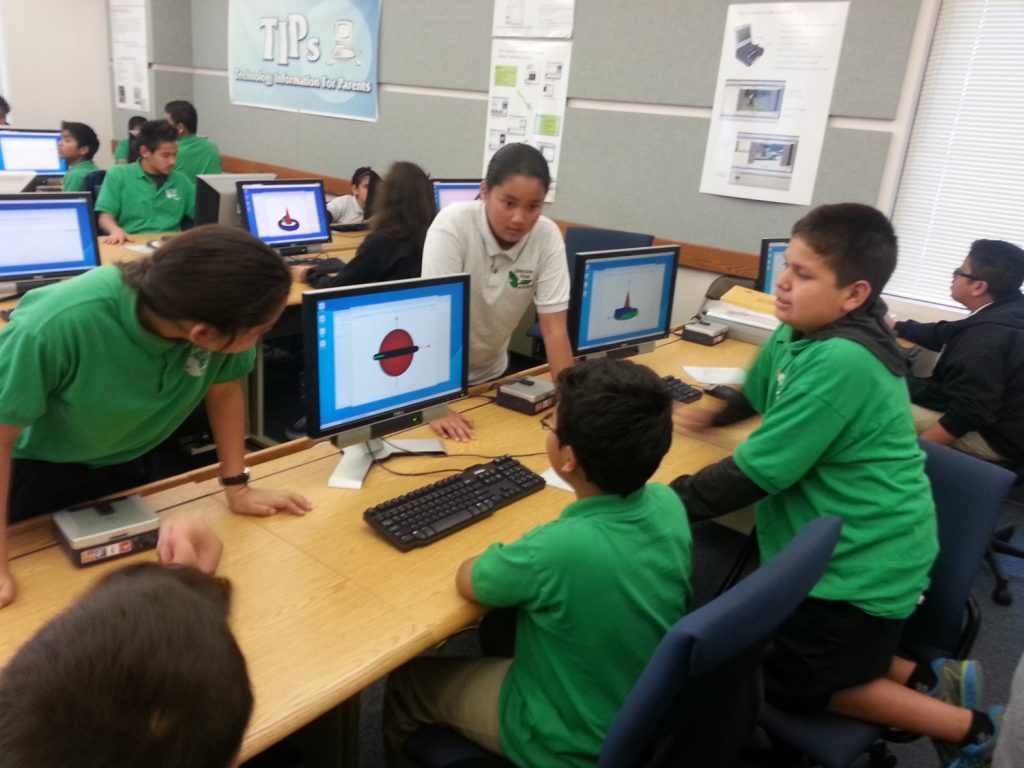
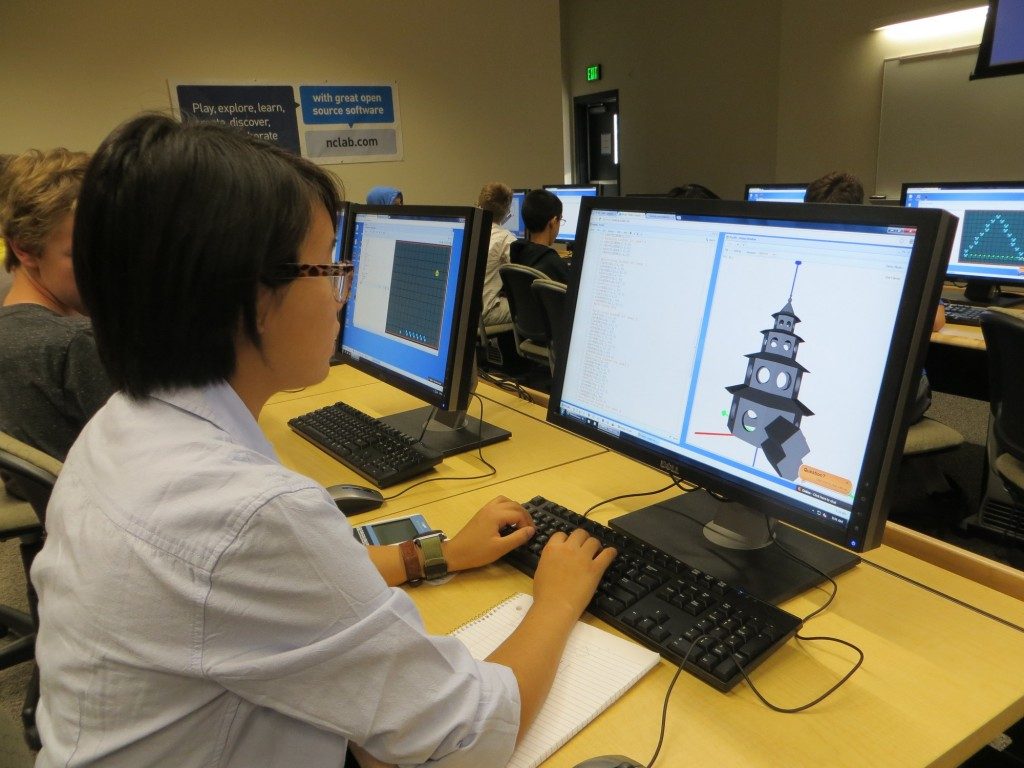
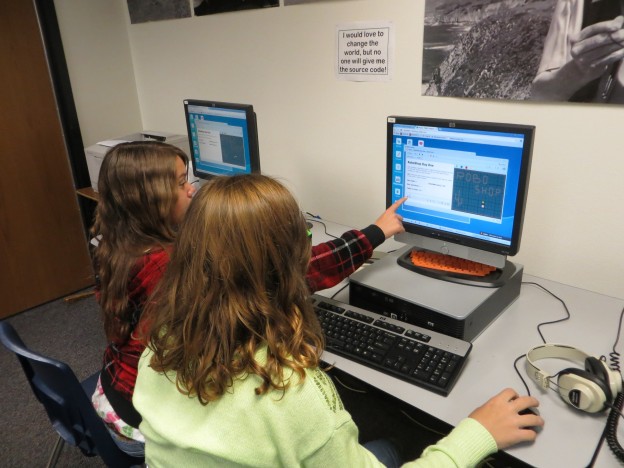
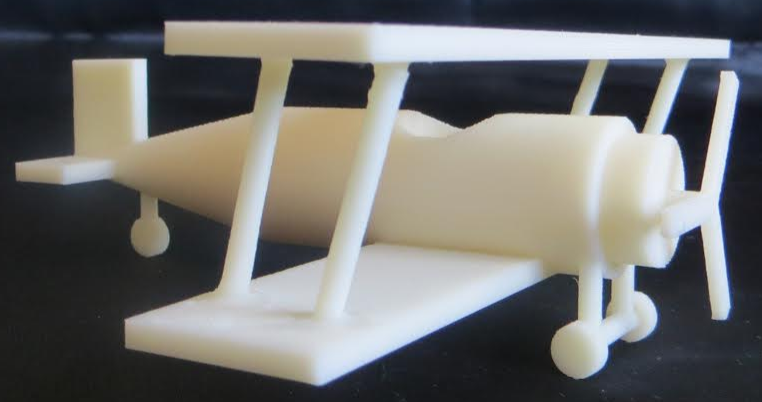
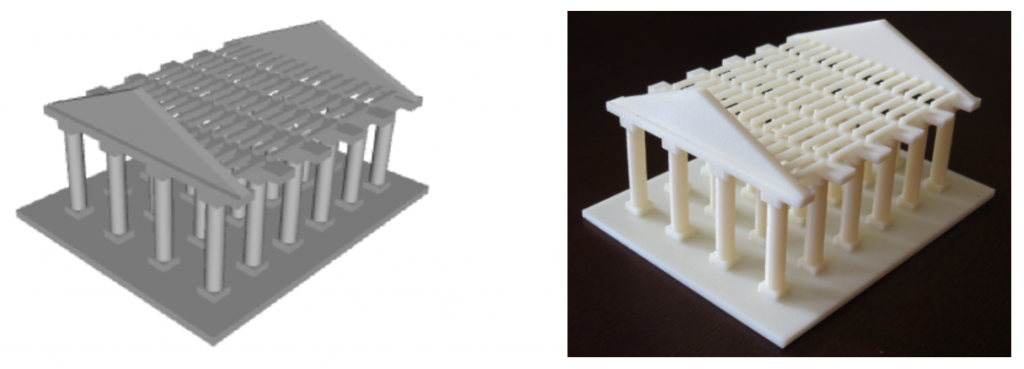
What It Means Use math to solve real-world problems, organize data, and understand the world around you. 3D Modeling Teaches Students to Understand the Real World Alex wants to build a 3D model of a biplane and print it on a 3D printer. In order to do this, he needs to learn a lot: Variety
3D #4: Model with Mathematics